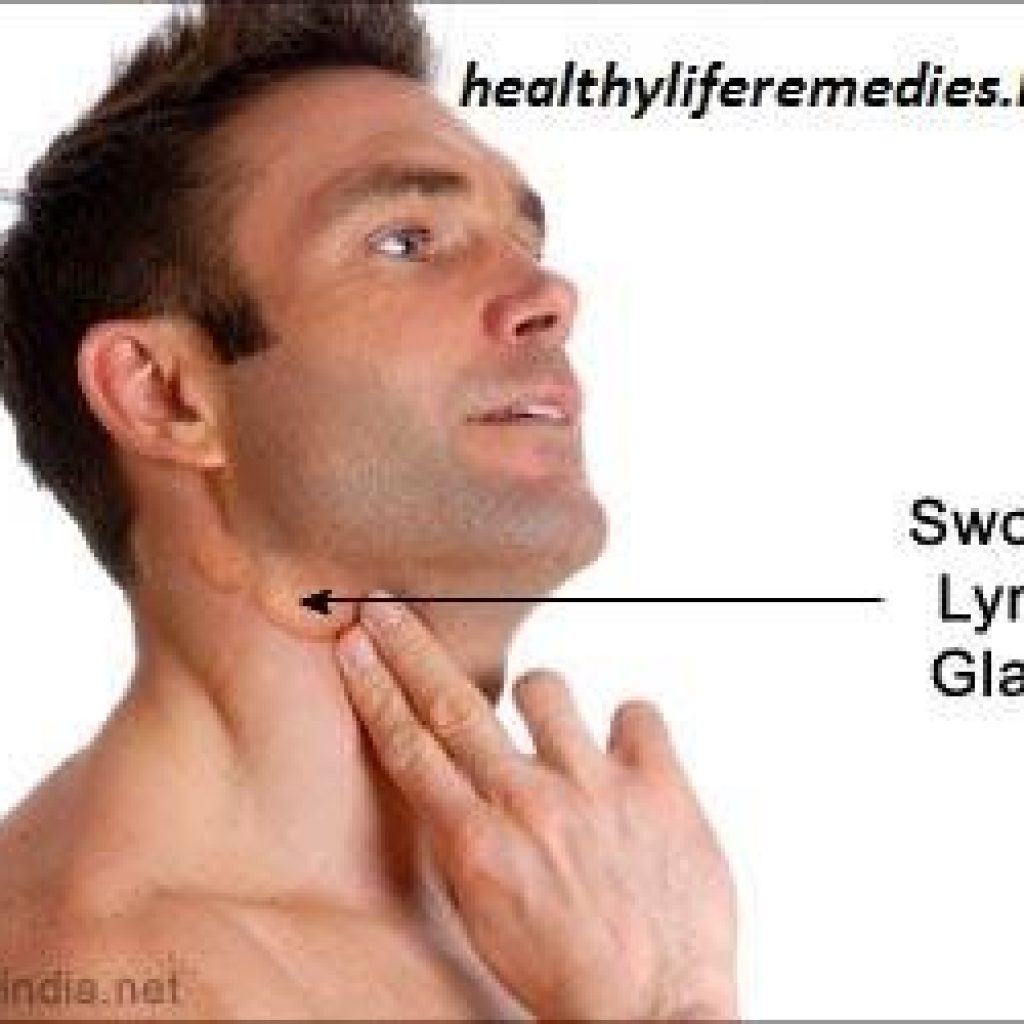
Most of patients have doubt about whether their lymh node enlargment is cancerous or not?i tried to give answer to their questions
WHAT IS LYMH SYSTEM ?How is cancer in lymph nodes found?Our bodies have a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. This network is a part of the body’s immune system. It collects fluid, waste material, and other things (like viruses and bacteria) that are in the body tissues, outside the bloodstream.Lymph vessels are a lot like the veins that collect and carry blood through the body. But instead of carrying blood, these vessels carry the clear watery fluid called lymph.Lymph fluid flows out from capillary walls to bathe the body’s tissue cells. It carries oxygen and other nutrients to the cells, and carries away waste products like carbon dioxide (CO2) that flow out of the cells. Lymph fluid also contains white blood cells, which help fight infections.Lymph fluid would build up and cause swelling if it were not drained in some way. That’s the role of the lymph vessels. Lymph vessels draw up the lymph fluid from around the cells to send it towards the chest. There, lymph fluid collects into a large vessel that drains into a Lymph nodes and what they do.Lymph vessels route lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for harmful substances. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas. The lymph fluid slowly flows in from all around the body, making its way back to the chest. At the end of its journey, the filtered fluid, salts, and proteins are dumped back into the bloodstream.Swollen lymph nodesWhen there’s a problem, such as infection, injury, or cancer, the node or the group of lymph nodes in that area may swell or enlarge as they work to filter out the “bad” cells. This may be called lymphadenopathy (LIMF-ad-uh-NOP-uh-thee). Swollen lymph nodes tell you that something is not right, but other symptoms help pinpoint the problem. For instance, ear pain, fever, and enlarged lymph nodes near your ear are clues that you may have an ear infection or cold.
WHAT IS THE CAUSES OF SWOLLEN LYMPH NODE???
Lymph nodes often swell in one location when a problem such as an injury, infection, or tumor develops in or near the lymph node. Which lymph nodes are swollen can help identify the problem.⦁ The glands on either side of the neck, under the jaw, or behind the ears commonly swell when you have a cold or sore throat. Glands can also swell following an injury, such as a cut or bite, near the gland or when a tumor or infection occurs in the mouth, head, or neck.
What causes swollen lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes often swell in one location when a problem such as an injury, infection, or tumor develops in or near the lymph node. Which lymph nodes are swollen can help identify the problem.⦁ The glands on either side of the neck, under the jaw, or behind the ears commonly swell when you have a cold or sore throat. Glands can also swell following an injury, such as a cut or bite, near the gland or when a tumor or infection occurs in the mouth, head, or neck.⦁ Glands in the armpit (axillary lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection to the arm or hand. A rare cause of axillary swelling may be breast cancer or lymphoma.⦁ The lymph nodes in the groin (femoral or inguinal lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection in the foot, leg, groin, or genitals. In rare cases, testicular cancer, lymphoma, or melanoma may cause a lump in this area.⦁ Glands above the collarbone (supraclavicular lymph nodes) may swell from an infection or tumor in the areas of the lungs, breasts, neck, or abdomen.Glands in the armpit (axillary lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection to the arm or hand. A rare cause of axillary swelling may be breast cancer or lymphoma.⦁ The lymph nodes in the groin (femoral or inguinal lymph nodes) may swell from an injury or infection in the foot, leg, groin, or genitals. In rare cases, testicular cancer, lymphoma, or melanoma may cause a lump in this area.⦁ Glands above the collarbone (supraclavicular lymph nodes) may swell from an infection or tumor in the areas of the lungs, breasts, neck, or abdomen.
CANCER IN THE LYMH NODE;Cancer can appear in the lymph nodes in 2 ways: it can either start there or it can spread there from somewhere else.Cancer that starts in the lymph nodes is called lymphoma. You can read more about lymphoma in Hodgkin Disease and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.More often, cancer starts somewhere else and then spreads to lymph nodes. That is the focus of this section.How does cancer spread to lymph nodes?Cancer can spread from where it started (the primary site) to other parts of the body.When cancer cells break away from a tumor, they can travel to other areas of the body through either the bloodstream or the lymph system. Cancer cells can travel through the bloodstream to reach distant organs. If they travel through the lymph system, the cancer cells may end up in lymph nodes. Either way, most of the escaped cancer cells die or are killed before they can start growing somewhere else. But one or two might settle in a new area, begin to grow, and form new tumors. This spread of cancer to a new part of the body is called metastasis.In order for cancer cells to spread to new parts of the body, they have to go through several changes. They first have to become able to break away from the original tumor and then attach to the outside wall of a lymph vessel or blood vessel. Then they must move through the vessel wall to flow with the blood or lymph to a new organ or lymph node.When cancer grows inside lymph nodes, it usually affects the lymph nodes near the tumor itself. These are the nodes that have been doing most of the work to filter out or kill the cancer cells.How is cancer in lymph nodes found?Normal lymph nodes are tiny and can be hard to find, but when there’s infection, inflammation, or cancer, the nodes can get larger. Those near the body’s surface often get big enough to feel with your fingers, and some can even be seen. But if there are only a few cancer cells in a lymph node, it may look and feel normal. In that case, the doctor must check for cancer by removing all or part of the lymph node.When a surgeon operates to remove a primary cancer, one or more of the nearby (regional) lymph nodes may be removed as well. Removal of one lymph node is called a biopsy. When many lymph nodes are removed, it’s called lymph node sampling or lymph node dissection. When cancer has spread to lymph nodes, there’s a higher risk that the cancer might come back after surgery. This information helps the doctor decide whether more treatment, like chemo or radiation, might be needed after surgery.Doctors may also take samples of one or more nodes using needles. Usually, this is done on lymph nodes that are enlarged. This is called a needle biopsy. The tissue that’s removed is looked at under the microscope by a pathologist (a doctor who diagnoses illness using tissue samples) to find out if there are cancer cells in itUnder the microscope, any cancer cells in the nodes look like the cancer cells from the primary tumor. For instance, when breast cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, the cells in the nodes look like breast cancer cells. The pathologist prepares a report, which details what was found. If a node has cancer in it, the report describes what it looks like and how much was seen.
SOME SPECIAL HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINE FOR GLANDULAR SWELLING:
Medicines are used only with instrections of a homeopathic doctor,because for each swelling have underline causes.so only take medicine after finding out correct reason .
BELLADONNAThe remedy in all glandular swellings of an inflammatory character with rapid swelling threatening suppuration. Swollen glands in the axillary region, especially at the climaxis, or swellings of the mammae, which are heavy, red and sensitive. Red shining streaks radiating from the glands with great heat and stitching pains indicate Belladonna. Swelling, suppuration and induration of the inguinal or cervical glands are well met by the remedy when the attack is acute and very painful. The glands, though swollen, are never purple or gangrenous; the inflammation involves the substance of a gland, Apis more the surface.IODINThis remedy corresponds to indolent swellings,those that are torpid and sluggish, which are large, hard and usually painless, and especially about the neck, or they may be anywhere. It has been used with some success in the parenchymatous form of goitre with obstructed breathing, but Bayes thinks it will rarely cure alone. Enlarged bronchial and mesenteric glands. Scrofulous or arthritic enlargement of the glands.SPONGIA. [Spong] Goitre hard and large with suffocative attacks; swelling in cervical region with tension and painful to touch. Graphites. Enlargement of glands of neck and axilla and mesenteric glands, patient debilitated; the swelling is painful and sensitive and is usually associated with some skin affection. There is great tendency in such patients to take cold.SILECIA. [Sil] Suppurating glands. Inflammation of the breast. Suppurative inflammations of the sebaceous glands also call for the remedy. Fistulous openings leading down to the glands is a specially useful indication
CALCARIA FLUORICA. [Calc-f] Long lasting and indolent glandular enlargements of the cervical lymphatic glands where the hardness is pronounced. Also enlargements of the bronchial and mesenteric glands, worse in damp weather, better from hot fomentations and rubbing,the 6X works well. Solidified indurations. Cistus. Glandular enlargement, especially of sub-maxillary glands with caries of the jaw. Scrofulous glandular swellings; an impure breath is an indication. The glands become inflammed. indurated and ulcerated.
CONIUM. [Con] In the 30th potency this remedy has a distinct, positive and marvelous power over certain glandular enlargements; possibly the 200th may do the same, but the 30th I know will do it. It will absorb hard glandular tumors, growths that can be outlined and felt. Enlargements of glands with little or no pain; it is useful for the beginning of scirrhus and especially is it indicated after injuries to glands, where stony hardness is present. Adenoma. Debilitated subjects with marked tendency to induration, extending to cellular tissue, swollen glands after burns, painless or sharp knife-like pains especially of mammary glands, but not confined to any special region.
SULPHUR.[Sulph] The great remedy for scrofulous glandular enlargements; the inguinal, axillary, sub-maxillary and subcutaneous glands are effected and the patient is of the typical Sulphur temperament. Baryta muriate and iodide have a special power over the absorbents; the muriate is especially for stony hardness.